
If there is no production output, then there would be no variable overhead costs. A manufacturing overhead budget covers all fixed, variable and applied manufacturing overhead costs of an organization. These costs are then allocated to each unit that’s produced and documented as part of the cost of goods sold in a manufacturer’s master budget.
Determination and Evaluation of Overhead Variance
- You also need to closely monitor your production schedule so you can make adjustments as needed.
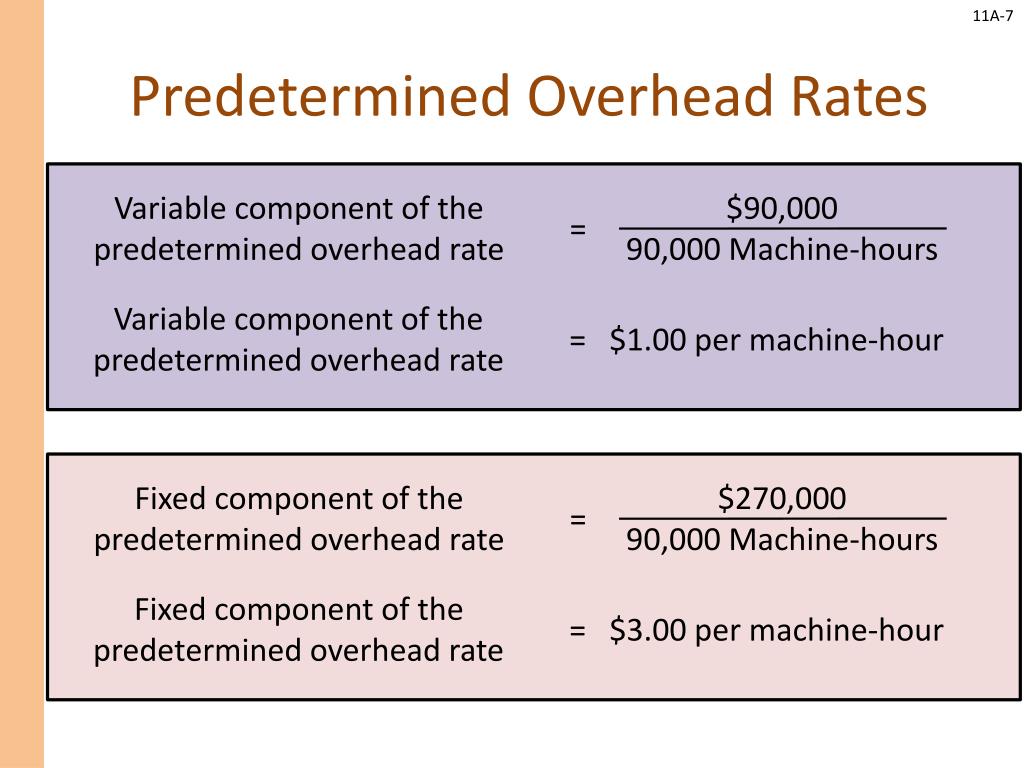
- The standard overhead rate is the total budgeted overhead of \(\$10,000\) divided by the level of activity (direct labor hours) of \(2,000\) hours.
- As a result, the variable overhead expenses must be included in the calculation of the cost per unit to ensure accurate pricing.
- You add the hourly rate of your work and then assign their hours, which will then populate the Gantt and the sheet view (like the Gantt but without a graphic timeline).
- Employee training and involvement are equally important in managing these costs.
You can calculate applied manufacturing overhead by multiplying the overhead allocation rate by the number of hours worked or machinery used. So if your allocation rate is $25 and your employee works for three hours on the product, your applied manufacturing overhead for this product would be $75. The labor involved in production, or direct labor, might not be variable cost unless the number of workers increases or decrease with production volumes.
What is the predetermined overhead rate?
There are also workflow automation and task authorization features to free up your workers to focus on what matters without jeopardizing quality. Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Variable overhead definition
While we have many project views, the kanban board contains key details on how much you’re spending on production. Use it to centralize manufacturing processes and collaborate with your team so you know how much you’re spending during production. Explore the intricacies of variable manufacturing overhead, including its elements, cost implications, and effective management strategies for businesses.
Indirect Materials
Accurately calculating your company’s manufacturing overhead costs is important for budgeting. Including only direct or “operational” expenses in your financial plan can leave the company in a major cash crunch, as every business in every industry has to incur some overhead costs. Calculating these beforehand can help you plan better and reduce unexpected expenses. Variable overhead costs are costs that change as the volume of production changes or the number of services provided changes. Variable overhead costs decrease as production output decreases and increase when production output increases.
Variable Overhead Spending Variance: Definition and Example
These include rental expenses (office/factory space), monthly or yearly repairs, and other consistent or “fixed” expenses that mostly remain the same. For example, you have to continue paying the same amount for renting office or factory space even if your company decides to lower production for this quarter. Manufacturing overhead costs are the indirect expenses required to keep a company operational. Even though all businesses have some manufacturing overhead costs, not all of them are equal.
This variance is unfavorable for Jerry’s Ice Cream becauseactual costs of $100,000 are higher than expected costs of$94,500. There are many costs that occur during production that it can be hard to track them all. Variable overhead is typically aggregated into the cost of goods sold, and so is not shown separately in the income statement. However, it may be listed as a separate line item in the cost of goods manufactured schedule, which is internal to the accounting department; it is not included in a company’s financial statements. This not only helps you run your business more effectively but is instrumental in making a budget. Knowing how much money you need to set aside for manufacturing overhead will help you create a more accurate budget.
Usually, the level of activity is either direct labor hours or direct labor cost, but it could be machine hours or units of production. In a standard cost system, overhead is applied to the goods based on a standard overhead how do federal income tax rates work rate. The standard overhead rate is calculated by dividing budgeted overhead at a given level of production (known as normal capacity) by the level of activity required for that particular level of production.
Variable manufacturing overhead costs are a set of expenses that fluctuate as production levels change. Businesses calculate and use variable manufacturing overhead to estimate future costs and analyze past performance. If variable manufacturing costs are significantly different than expected, the business will perform variance analysis to identify the underlying cause.